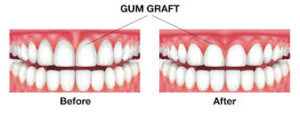
 Your gums support and shield each and every tooth in your mouth. A healthy smile requires more than just white, perfectly aligned teeth. Gum recession gradually erodes and causes discomfort, sensitivity, and changes that may impact confidence and health. Gum grafting is more than just a dental procedure. It is a chance to protect your teeth, heal your gums, and bring back the natural beauty of your smile. This blog will discuss the significance of gums, the causes of their recession, and the ways in which contemporary grafting might contribute to long lasting results at Bel Air MD Dentist.
Your gums support and shield each and every tooth in your mouth. A healthy smile requires more than just white, perfectly aligned teeth. Gum recession gradually erodes and causes discomfort, sensitivity, and changes that may impact confidence and health. Gum grafting is more than just a dental procedure. It is a chance to protect your teeth, heal your gums, and bring back the natural beauty of your smile. This blog will discuss the significance of gums, the causes of their recession, and the ways in which contemporary grafting might contribute to long lasting results at Bel Air MD Dentist.
What Is Gum Grafting?
A specialist dentistry procedure called gum grafting is used to address gum recession by regrowing tissue in areas where the gums have receded or worn away. This tissue is frequently carefully positioned over exposed tooth roots after being removed from the roof of the mouth or another donor source. Rebuilding lost gum tissue, protecting delicate dental roots, and preventing further recession are the key objectives. Visit Bel Air MD Dentist and get cost effective gum graft treatment.
Why Gums Recede
The reasons are given below:
Periodontal Disease
One of the most significant causes of gum recession is periodontal disease. Gums separate and expose tooth roots as a result of the destruction of the bone and supportive tissues surrounding teeth.
Aggressive Brushing Habits
Gum tissue is gradually worn down by aggressive tooth brushing or by using a toothbrush with hard bristles. Although the aim of this habit is to keep teeth clean, and pull gums back.
Genetic Predisposition
Some people’s gum tissue is inherently thinner or more sensitive. Even with good dental hygiene, some people’s gums still recede more easily, which is due to genetics.
Orthodontic Treatment or Trauma
Gum position can occasionally be impacted by orthodontic movement or accidental injury. Gums recede when teeth shift quickly or experience trauma, because the surrounding gum tissue may not adapt fast enough.
Different Types of Gum Grafts
The Following are the types of gum graft:
Connective Tissue Graft
Using this procedure, the dentist removes tissue under the palate’s outer layer. The exposed roots are then covered by this tissue. It integrates well and produces results that look natural. Dentists commonly use this procedure.
Free Gingival Graft
A thin layer of tissue extracted directly from the palate and used in the area where gums recede by dentists. It usually makes the weak gums stronger and prevents further recession.
Pedicle Graft
The dentist uses the surrounding gums to create a gum tissue layer during this treatment. The exposed root is then covered by this tissue layer. When there is sufficient gum tissue surrounding the tooth, this procedure works perfectly.
Allografts and Alternatives
Instead of using the patient’s own tissue, dentists occasionally employ donor tissue or specifically prepared graft tissues. These choices decrease discomfort and prevent the need to remove tissue from the palate.
How the Procedure Works
Consultation and Treatment Planning
A comprehensive consultation is the first step in the process. The dentist talks about your objectives and problems while examining your mouth and measuring gum recession. X-rays can be used to assess the condition of the bones and teeth. You and your dentist work together to determine the best type of transplant for your condition.
Harvesting Graft Tissue or Using Donor Material
Depending on the type of graft, the dentist carefully takes a tiny portion from the roof of your mouth, either directly from the surface layer or from behind it. Sometimes the dentist applies synthetic material or processed donor tissue. These treatments decrease discomfort and eliminate the need to take oral tissue samples.
Placement and Suturing
The dentist carefully covers the exposed root or thinning gum with the graft when it is ready. Small sutures hold the graft and help it bond to the underlying gum tissue. To ensure that the new tissue matches existing tissues naturally and protects the roots, this process needs to be done carefully.
Post-Procedure Care
The dentist will provide you instructions on how to care for your mouth during the healing process after the surgery. You are told to use special mouth washes to keep the area clean, avoid brushing close to the graft site, and eat soft foods. Regular follow-up appointments help the dentist to assess healing and, if necessary, remove stitches.
Is Gum Grafting Right for You?
Gum grafting is not necessary for everyone, but for many, it is a common step in preserving their teeth and enhancing their facial appearance. Knowing who benefits most and what factors may affect the procedure helps in making an informed decision.
Indications and Candidacy
People with visible gum recession, exposed tooth roots, or thinned gum tissue benefit from gum grafting. It helps people who want to smooth out an uneven gum line or who have dental sensitivity as a result of exposed roots. Gum grafting is commonly recommended by dentists to prevent further recession of teeth, decrease sensitivity, and promote improved oral health. Patients for this procedure are often those who maintain good oral hygiene and have healthy teeth.
Considerations for Smokers and Patients with Medical Conditions
Smoking has an adverse effect on healing and reduces gum transplant success rates. To help the graft take hold and heal properly, dentists usually recommend stopping smoking both before and after treatment. The procedure and recovery may also be impacted by certain medical conditions, including uncontrolled diabetes, immune system disorders, or blood clotting issues. In these situations, the dentist talks about the risks, consults with your doctor if necessary, and helps in determining whether gum grafting is still a safe option.
How to Avoid Needing a Gum Graft
- Maintaining good gum health and lowering your risk of requiring a gum transplant in the future can be achieved with daily routines and efficient treatment.
- Avoid brushing your teeth too often. Use a toothbrush with soft bristles and brush gently in circular strokes. It efficiently cleans teeth without causing harm to the gum line.
- Visit your dentist on a regular basis for examinations and professional cleanings. Regular checkups facilitate the early diagnosis of gum disease or recession, allowing for rapid treatment.
- Keep an eye out for any bleeding, swelling, or redness that may indicate gum disease. Gums remain smooth and healthy with early therapy, which also helps stop the condition from getting worse.
FAQs
Is gum grafting painful?
Because the dentist uses local anesthetics to numb the area, the treatment itself is typically painless. Following surgery, some little soreness or swelling may occur, but most individuals can easily manage it with painkillers and by adhering to aftercare recommendations.
How long does it take to heal after gum grafting?
It usually takes one to two weeks for the epithelialization to occur. It can take a few weeks for the graft to fully heal and merge with the surrounding tissue. Your dentist arrange follow-up appointments to assess your progress.
Will the new gum tissue look natural?
Yes, particularly if your own tissue is used for the graft. To ensure that the graft blends in smoothly and appears natural, dentists carefully position and shape it to match your natural gum line.
Can gum grafting stop further gum recession?
Gum grafting can prevent further recession in treated regions and help cover exposed roots. To maintain long-term gum health, it is essential to maintain proper oral hygiene and schedule routine dental exams.
Is gum grafting covered by insurance?
Gum grafting is often covered by dental insurance policies if it is required for medical reasons, such as avoiding tooth loss or correcting recession. The best course of action is to verify your coverage by consulting your plan or by contacting your dentist’s insurance office.






